The history of human civilization spans thousands of years, encompassing a diverse array of cultures, innovations, and societies. This article explores some of the oldest civilizations in history, from the ancient Sumerians of Mesopotamia to the Aboriginal Australians, offering insights into their unique contributions to human development.
The Sumerians: Pioneers of Civilization
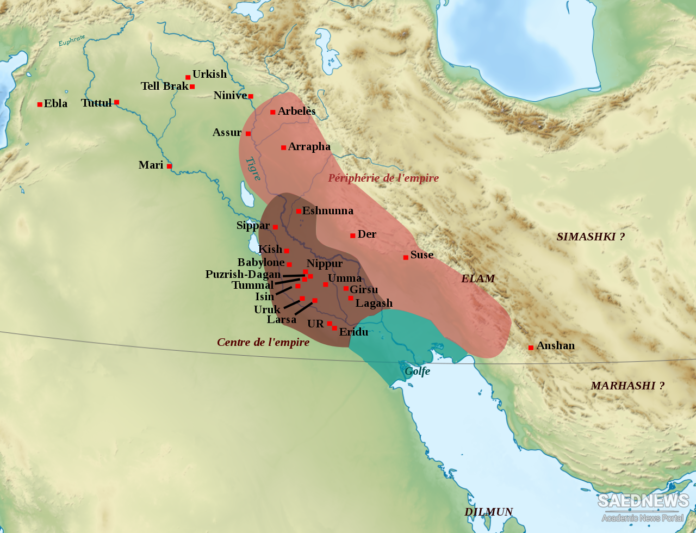
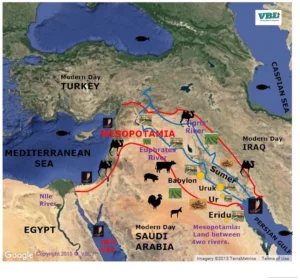
The Sumerians, who settled in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) around 4500 BCE, are often credited with creating one of the first true civilizations. Known for their advanced urban planning, they established city-states such as Ur, Uruk, and Eridu.
Key Contributions:
- Writing System: The Sumerians developed cuneiform, one of the earliest known writing systems, which was used for record-keeping, literature, and administrative purposes.
- Architecture: They built ziggurats, massive terraced structures that served religious purposes.
- Legal Codes: The Code of Ur-Nammu, one of the earliest legal codes, established laws and justice systems.
The Egyptians: Masters of Monumental Architecture
Ancient Egypt, emerging around 3100 BCE along the Nile River, is renowned for its monumental architecture and sophisticated society. The civilization lasted for millennia, leaving an indelible mark on history.
Key Contributions:
- Pyramids: The construction of the pyramids, especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, exemplifies their architectural prowess.
- Hieroglyphics: Their unique writing system, hieroglyphics, was used in religious texts, tombs, and monuments.
- Advancements in Medicine and Engineering: Egyptians made significant contributions to medicine, engineering, and mathematics.
The Indus Valley Civilization: Urban Planning and Trade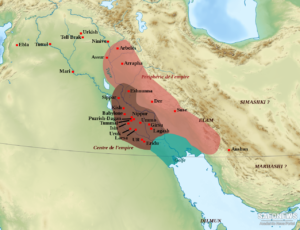
The Indus Valley Civilization, which flourished around 2600 BCE in present-day Pakistan and northwest India, is noted for its advanced urban planning, architecture, and social organization.
Key Contributions:
- Urban Planning: Cities like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa featured grid layouts, advanced drainage systems, and standardized brick sizes.
- Trade Networks: They had extensive trade networks with Mesopotamia and other regions.
- Undeciphered Script: Despite numerous artifacts, their writing system remains undeciphered, adding a layer of mystery to their culture.
The Ancient Chinese Civilization: Dynastic Rule and Innovations
Ancient China, with a history dating back to around 2100 BCE, saw the rise of powerful dynasties such as the Xia, Shang, and Zhou, each contributing to the development of Chinese culture, philosophy, and technology.
Key Contributions:
- The Great Wall: A monumental defense structure to protect against invasions.
- Philosophical Thought: The development of Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism profoundly influenced Chinese society.
- Innovations: Significant inventions include paper, gunpowder, the compass, and printing.
The Minoans: Europe’s First Advanced Civilization
The Minoans, who flourished on the island of Crete around 2000 BCE, are considered Europe’s first advanced civilization. Known for their vibrant art and advanced architecture, the Minoans played a crucial role in the development of Greek culture.
Key Contributions:
- Palatial Structures: The palace at Knossos is a prime example of their architectural skills.
- Art and Pottery: Their art, particularly frescoes, depicted religious rituals and daily life.
- Trade and Economy: They established extensive trade networks across the Mediterranean.
The Aboriginal Australians: A Continuous Culture
The Aboriginal Australians, with a history spanning over 50,000 years, represent one of the oldest continuous cultures on Earth. They have maintained a deep connection to their land, spirituality, and traditional practices.
Key Contributions:
- Oral Traditions and Stories: Their rich oral traditions and Dreamtime stories offer insights into their worldview and history.
- Art and Rock Paintings: Aboriginal art, especially rock paintings, are some of the oldest known artworks.
- Environmental Management: Practices like controlled burning, known as “fire-stick farming,” demonstrate sophisticated land management techniques.
Conclusion
The exploration of these ancient civilizations reveals the incredible diversity and ingenuity of early human societies. From the pioneering Sumerians and the monumental achievements of the Egyptians to the sophisticated urban planning of the Indus Valley and the continuous culture of the Aboriginal Australians, each civilization has left a lasting legacy that continues to influence our world today.